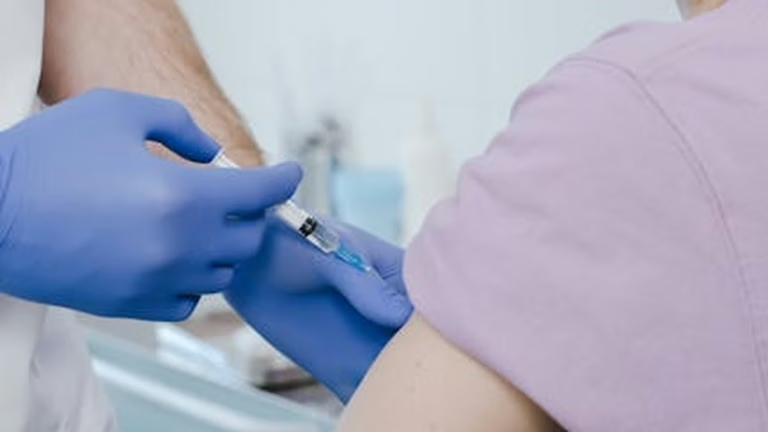
Flu Season 2025: Updated Vaccine Recommendations and Preventive Measures
Flu season is a recurring concern, and staying informed is crucial for protecting yourself and your loved ones. As we approach flu season 2025, understanding the updated vaccine recommendations and implementing effective preventive measures is more important than ever. This guide provides comprehensive information to help you navigate the upcoming season and minimize your risk of contracting the flu.
Understanding the Flu and Its Impact
The flu, or influenza, is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. It can cause mild to severe illness, and at times can lead to serious complications, hospitalization, or even death. The flu virus is constantly changing, which is why a new flu vaccine is developed each year to target the strains expected to be most prevalent.
Why is Flu Season a Concern?
Flu season typically peaks during the fall and winter months. The colder weather often leads to people spending more time indoors, increasing the likelihood of close contact and virus transmission. This, combined with the virus’s ability to mutate, makes annual flu vaccination and preventive measures essential.
Flu Vaccine Recommendations for 2025
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and other health organizations provide annual recommendations on who should receive the flu vaccine. Staying updated with these recommendations is crucial for making informed decisions about your health.
Who Should Get Vaccinated?
The CDC generally recommends that everyone 6 months of age and older should receive a flu vaccine each year. There are, however, some specific groups for whom vaccination is particularly important:
- Young children: Children under 5 years old are at higher risk of developing serious flu complications.
- Pregnant women: Flu vaccination during pregnancy can protect both the mother and the newborn.
- Older adults: Individuals aged 65 years and older are more likely to experience severe illness from the flu.
- People with chronic health conditions: Those with conditions like asthma, diabetes, heart disease, or lung disease are at increased risk.
- Healthcare workers: Vaccinating healthcare workers helps protect themselves and their patients.
Types of Flu Vaccines Available
Several types of flu vaccines are typically available, including:
- Inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV): Given as a shot, this vaccine contains inactivated (killed) flu viruses.
- Recombinant influenza vaccine (RIV): Also given as a shot, this vaccine is produced using recombinant technology and does not contain flu viruses.
- Live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV): Administered as a nasal spray, this vaccine contains a weakened (attenuated) live flu virus. The availability of LAIV may vary.
Consult with your healthcare provider to determine which vaccine is most appropriate for you based on your age, health status, and any allergies you may have.
Effective Preventive Measures
While the flu vaccine is a powerful tool for protection, adopting preventive measures can further reduce your risk of contracting and spreading the flu.
Everyday Habits for Flu Prevention
- Frequent handwashing: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after being in public places or touching surfaces that may be contaminated.
- Use hand sanitizer: When soap and water are not available, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol.
- Avoid touching your face: Avoid touching your eyes, nose, and mouth, as these are entry points for the virus.
- Practice respiratory etiquette: Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when you cough or sneeze. If a tissue is not available, cough or sneeze into your elbow rather than your hands.
- Stay home when sick: If you are feeling unwell, stay home from work, school, or other public places to prevent spreading the virus to others.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Get enough sleep, eat a balanced diet, and exercise regularly to support your immune system.
Environmental Measures
- Clean and disinfect surfaces: Regularly clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces, such as doorknobs, light switches, and countertops.
- Improve ventilation: Increase ventilation by opening windows or using air purifiers.
What to Do If You Get the Flu
Even with vaccination and preventive measures, you may still contract the flu. If you suspect you have the flu, it’s important to take appropriate action.
Seeking Medical Advice
Contact your healthcare provider promptly, especially if you are at high risk of complications. Antiviral medications can be effective in treating the flu, but they are most effective when started within 48 hours of symptom onset.
Home Care and Rest
If your symptoms are mild, you can manage them at home with rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, juice, or broth. Avoid contact with others to prevent spreading the virus.
Staying Informed and Prepared
Flu season 2025 is approaching, and preparation is key. By understanding the latest vaccine recommendations, implementing effective preventive measures, and knowing what to do if you get sick, you can significantly reduce your risk of contracting and spreading the flu. Stay informed by consulting with your healthcare provider and monitoring updates from reliable sources like the CDC. Prioritize your health and the health of those around you this flu season.