The Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Reduce Chronic Pain & Boost Your Health
What is Inflammation and Why Does it Matter?
Inflammation is a natural process that helps your body heal from injury and fight off infection. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can contribute to a wide range of health problems, including arthritis, heart disease, diabetes, and even some types of cancer. Many factors can contribute to chronic inflammation, including stress, lack of sleep, and, most importantly, diet.
The good news is that you can significantly reduce chronic inflammation and improve your overall health by adopting an anti-inflammatory diet. This isn’t a restrictive diet, but rather a way of eating that emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods rich in nutrients and antioxidants that help to quell inflammation.
Key Principles of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
The anti-inflammatory diet focuses on incorporating foods that fight inflammation and limiting those that promote it. Here are the core principles:
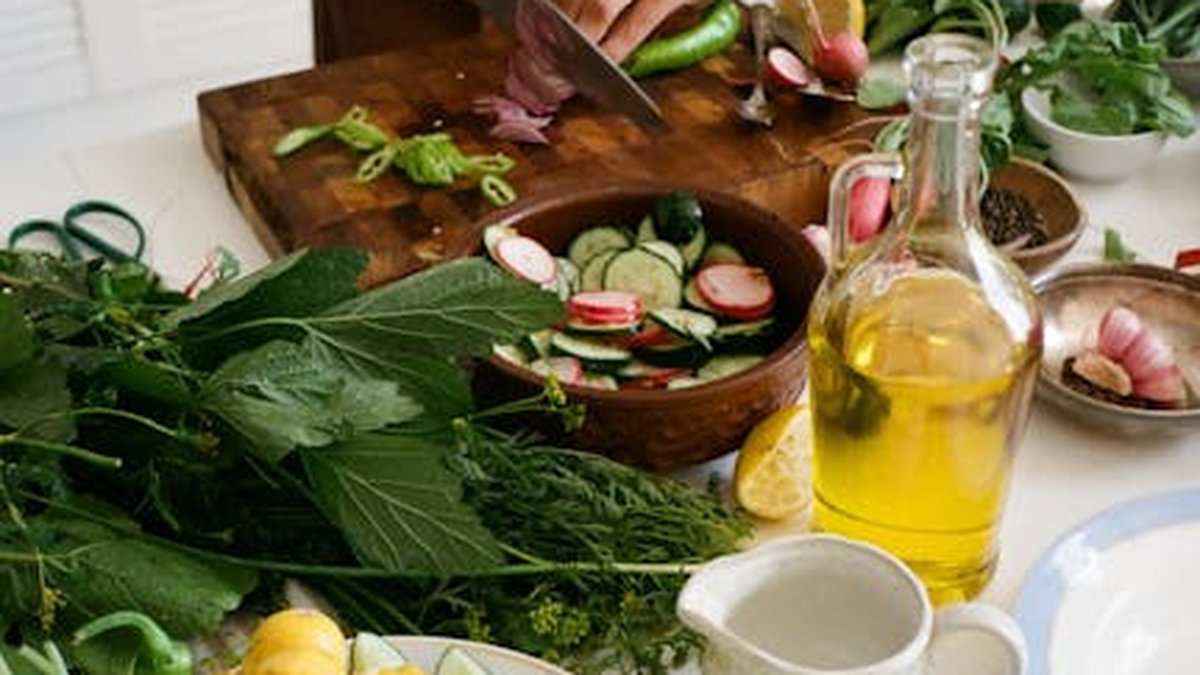
- Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods: Think fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Load up on fruits and vegetables: Aim for a rainbow of colors to get a variety of antioxidants.
- Choose healthy fats: Opt for sources like olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds.
- Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbohydrates: These can contribute to inflammation.
- Stay hydrated: Water is essential for overall health and helps flush out toxins.
Foods to Embrace
These foods are known for their anti-inflammatory properties:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have potent anti-inflammatory effects. Aim for at least two servings per week.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries are packed with antioxidants. Enjoy them as a snack, in smoothies, or on top of your oatmeal.
- Olive Oil: Extra virgin olive oil is a healthy fat source with powerful anti-inflammatory compounds. Use it for cooking, salad dressings, and drizzling over vegetables.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Add them to salads, smoothies, or stir-fries.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are good sources of healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants. Snack on them throughout the day or add them to your meals.
- Turmeric: This spice contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory compound. Add it to curries, soups, or smoothies. Consider taking a curcumin supplement for a more concentrated dose.
- Ginger: Another spice with anti-inflammatory properties. Use it in cooking, tea, or smoothies.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
These foods can contribute to inflammation and should be limited or avoided:
- Processed Foods: These are often high in unhealthy fats, sugar, and sodium.
- Sugary Drinks: Sodas, juices, and sweetened teas are loaded with sugar, which can promote inflammation.
- Refined Carbohydrates: White bread, pasta, and pastries are quickly digested and can lead to spikes in blood sugar, contributing to inflammation.
- Red Meat: Limit your intake of red meat, especially processed meats like bacon and sausage.
- Fried Foods: These are often cooked in unhealthy oils and can contribute to inflammation.
Practical Tips for Implementing the Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Making gradual changes to your diet is often more sustainable than trying to overhaul everything at once. Here are some practical tips to help you get started:
- Start small: Choose one or two changes to focus on each week. For example, you might start by adding a serving of berries to your breakfast each day or swapping out sugary drinks for water.
- Plan your meals: Meal planning can help you stay on track and avoid unhealthy choices.
- Read food labels: Pay attention to the ingredients list and nutritional information.
- Cook at home more often: This gives you more control over the ingredients you’re using.
- Find healthy substitutes: Swap out refined grains for whole grains, sugary drinks for water, and unhealthy fats for healthy fats. For example, use olive oil instead of vegetable oil, and choose whole-wheat bread over white bread.
Benefits Beyond Pain Relief
While the anti-inflammatory diet is often touted for its ability to reduce chronic pain, its benefits extend far beyond that. By reducing inflammation throughout the body, this way of eating can also:
- Improve gut health: Many anti-inflammatory foods are also rich in fiber, which is essential for a healthy gut.
- Boost your immune system: Antioxidants and other nutrients in anti-inflammatory foods can strengthen your immune system.
- Reduce your risk of chronic diseases: By reducing inflammation, you can lower your risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other chronic conditions.
- Improve your mood: Studies have shown that an anti-inflammatory diet can improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression.
Conclusion
The anti-inflammatory diet is a powerful tool for reducing chronic pain, improving overall health, and preventing disease. By focusing on whole, unprocessed foods and limiting inflammatory triggers, you can significantly improve your well-being. Remember to start small, be patient with yourself, and focus on making sustainable changes that you can stick with for the long term. Your body will thank you for it!